Understanding the Functional Role of Elevator Background Boards
Elevator background boards are structural and decorative panels installed on the inner walls of elevator cabins. Their primary role is to protect the cabin wall structure while creating a durable and visually cohesive interior. Unlike superficial decorative films, background boards act as a load-bearing surface that supports handrails, control panels, mirrors, and lighting components. In commercial buildings with high passenger flow, these boards must resist frequent contact, impact, and cleaning chemicals without warping or discoloration.
From a maintenance perspective, elevator background boards simplify repair and replacement. When surface damage occurs, individual panels can be removed without dismantling the entire cabin structure. This modular approach reduces downtime and ensures compliance with building management requirements. In residential elevators, background boards also contribute to noise reduction by dampening vibrations generated during vertical movement.
Common Materials Used in Elevator Background Boards
Material selection directly affects durability, fire resistance, weight, and long-term appearance. Elevator background boards are typically engineered using composite structures that balance strength with ease of installation. The most widely adopted materials are chosen based on building type, passenger volume, and interior design goals.
Stainless Steel Panels
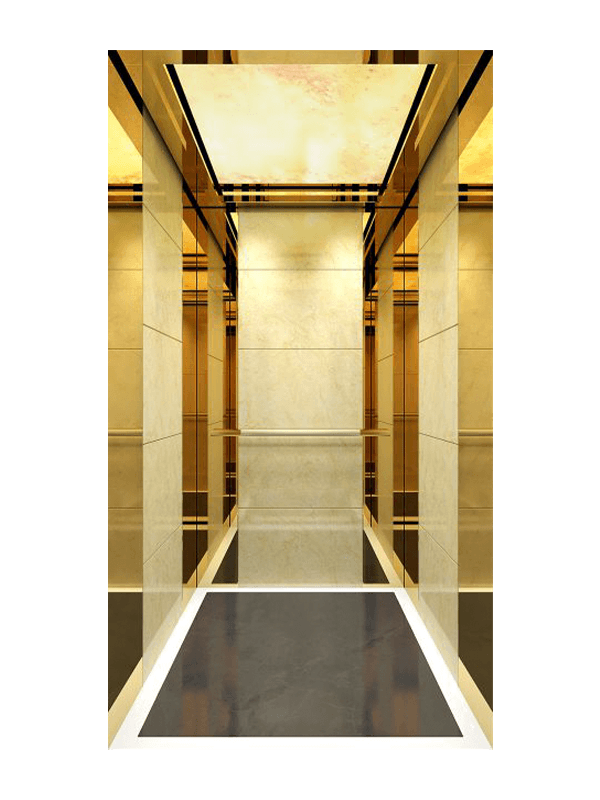
Stainless steel elevator background boards are widely used in commercial buildings, hospitals, and hotels. They offer excellent corrosion resistance, high impact strength, and ease of cleaning. Brushed, mirror, and etched finishes allow designers to adapt the surface to different architectural styles while maintaining consistent performance under heavy use.
PVC and Composite Boards
PVC-based elevator interior panels are lightweight and cost-effective. When reinforced with composite cores, these boards provide adequate rigidity for residential and low-traffic commercial elevators. Their moisture resistance makes them suitable for coastal or high-humidity environments where metal surfaces may require additional treatment.
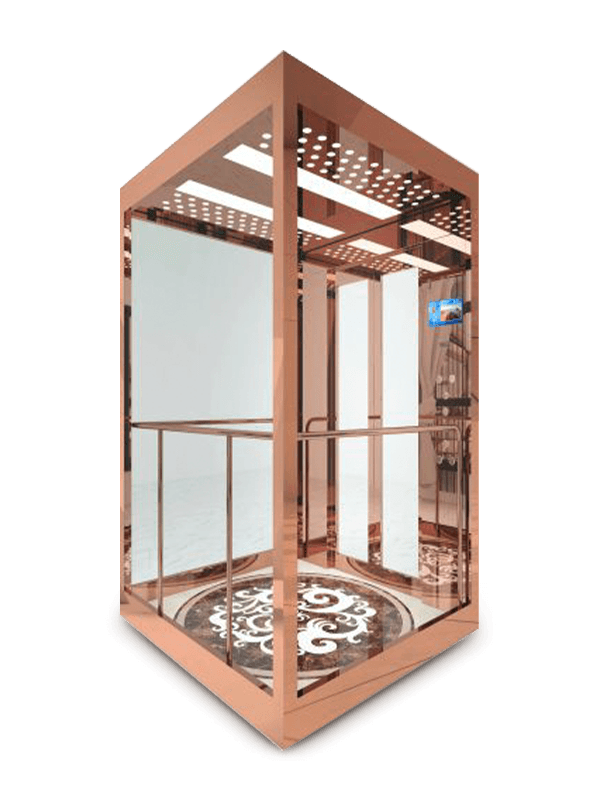
Glass and Laminated Panels
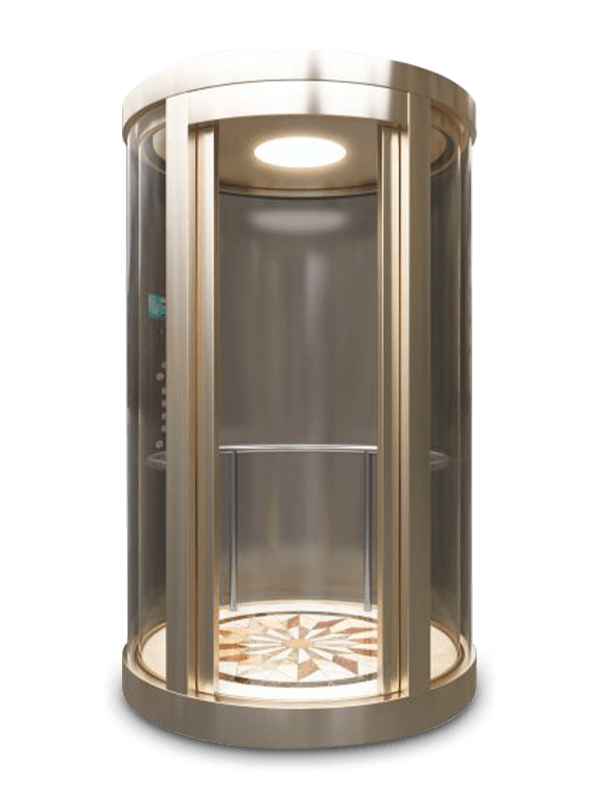
Laminated glass background boards are often used in panoramic elevators or high-end commercial projects. These panels combine tempered glass with safety interlayers, ensuring impact resistance and passenger safety. When paired with backlighting, glass boards enhance spatial perception within compact elevator cabins.
Structural Design and Thickness Considerations
The structural integrity of elevator background boards depends on panel thickness, core material, and mounting method. Standard thickness ranges from 6 mm to 18 mm, depending on the material composition and intended load. Thinner panels are suitable for decorative surfaces, while thicker boards are required where handrails or control modules are mounted.
Engineers must account for vibration, thermal expansion, and cabin movement during operation. Poorly designed background boards may loosen over time, creating noise or misalignment. Precision cutting and factory pre-drilled mounting points significantly improve long-term stability and reduce installation errors on-site.
Installation Methods for Elevator Background Boards
Proper installation ensures safety, durability, and ease of future maintenance. Elevator background boards are typically installed after the cabin frame is secured and electrical wiring is completed. Alignment accuracy at this stage directly influences the final appearance and functional performance.
- Mechanical fastening using concealed brackets for high-strength applications
- Adhesive bonding combined with safety clips for lightweight composite panels
- Modular rail systems allowing quick removal and replacement of individual boards
Installers should verify vertical alignment and expansion gaps to prevent stress concentration. Improper spacing may lead to surface cracking or audible friction during elevator operation. Following manufacturer installation guidelines is critical for maintaining warranty coverage.
Fire Safety and Regulatory Compliance
Elevator background boards must comply with fire safety standards such as flame spread, smoke density, and toxicity limits. In many regions, non-combustible or fire-retardant materials are mandatory for public buildings. Compliance ensures passenger safety and simplifies inspection approval during building certification.
Using certified materials also reduces liability risks for property owners. Fire-rated boards are typically tested as complete assemblies, meaning surface finishes, adhesives, and cores must work together to meet regulatory thresholds.
Maintenance and Lifecycle Cost Optimization
Well-designed elevator background boards reduce long-term maintenance costs. Smooth, non-porous surfaces resist staining and simplify daily cleaning. In high-traffic elevators, scratch-resistant coatings extend the aesthetic lifespan of panels without requiring frequent refinishing.
Lifecycle planning should include availability of replacement panels and standardized dimensions. Selecting widely used panel sizes allows building managers to source replacements quickly, minimizing elevator downtime and service disruption.
Material Comparison for Practical Selection
| Material Type | Durability | Maintenance | Typical Application |
| Stainless Steel | Very High | Low | Commercial Buildings |
| PVC Composite | Medium | Low | Residential Elevators |
| Laminated Glass | High | Medium | Panoramic Elevators |
Design Integration with Modern Elevator Cabins
Elevator background boards play a key role in cabin design coherence. Color, texture, and reflectivity influence passenger perception of space and cleanliness. Coordinating background boards with flooring, ceiling panels, and lighting systems results in a unified interior that aligns with the building’s overall architectural identity.
For modern elevators, modular background boards allow design updates without full cabin replacement. This flexibility is particularly valuable in hotels and office buildings where branding and interior trends evolve over time.







 English
English عربى
عربى Deutsch
Deutsch Español
Español Français
Français русский
русский 日本語
日本語 简体中文
简体中文